How is Moonshine Made?
Making alcohol revolves around
two processes: fermentation and distillation.
Fermentation
is a chemical reaction that occurs when the yeast breaks down
the sugar. One result of that reaction is alcohol.
Distillation is the process of evaporating the alcohol (which
boils at a lower temperature than water) and collecting the
steam before condensing it back into liquid form.
Here's the whole process, step by step:
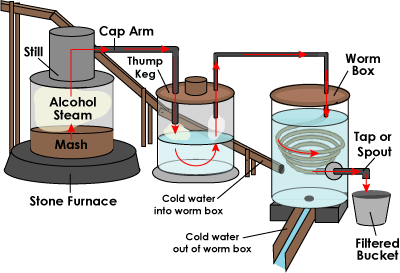
|
- The corn is ground into meal. Today, some
moonshiners use commercial hog feed because it's mostly made
of corn and is easy to buy without attracting a lot of
attention.
- The corn meal is soaked in hot water in the
still. Sometimes sugar is added (or even used instead of
grain), but traditional moonshiners added malt to
convert the starch in the corn meal into sugar. Then the
yeast is put in, which starts the fermentation
process. (See
How Beer
Works for details on the fermentation process.) This
mixture, called mash, is
stirred thoroughly and heated for a set amount of time in
the still. The still and all the metal piping used are made
of copper, which conducts heat well and doesn't leech into
the alcohol.
- The stone furnace beneath the still is brought up to
about 172 degrees Fahrenheit (78 C). Wood, coal and even
steam have been used in the past to heat the still, but most
moonshiners started using propane decades ago.
- The alcohol evaporates. As pressure builds in the
still, the alcohol steam is forced through the cap
arm, a pipe that leads out of the top of the still.
- Some moonshiners use a thump keg, which is simply
a heated barrel into which the steam is forced. Some
solid material from the mash usually comes along with
the steam, so the thump keg, so named for the thumping sound
the bits of mash make when they drop into the barrel,
re-evaporates the alcohol, filtering out the mash. If
a moonshiner wants to make his or her alcohol extra potent,
he or she might "charge" the thump keg -- add undistilled
mash or a few gallons of alcohol into the keg so the steam
picks up extra alcohol vapor on its way to the worm box.
- The steam travels into the worm, a coiled length
of pipe that winds down the inside of the worm box.
The worm box is a crate or barrel that has cold water,
usually diverted from a nearby creek, flowing into the top
and then back out the bottom. This keeps the worm bathed in
constantly circulating cold water, which condenses the
alcohol steam into liquid.
- A spout, tap, or hose leads from the end of the
worm into a bucket, usually through one last filter.
- The resulting clear liquid is ready to be
illegally bottled and sold.
Next, we'll see what makes moonshine different from
store-bought liquor.
Here are some interesting links:
